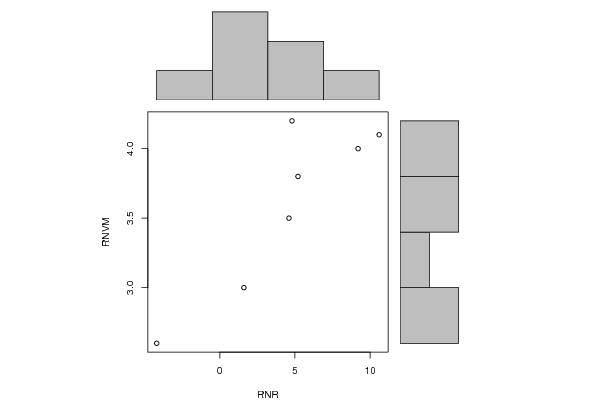
bitmap(file='test1.png')
histx <- hist(x, plot=FALSE)
histy <- hist(y, plot=FALSE)
maxcounts <- max(c(histx$counts, histx$counts))
xrange <- c(min(x),max(x))
yrange <- c(min(y),max(y))
nf <- layout(matrix(c(2,0,1,3),2,2,byrow=TRUE), c(3,1), c(1,3), TRUE)
par(mar=c(4,4,1,1))
plot(x, y, xlim=xrange, ylim=yrange, xlab=xlab, ylab=ylab)
par(mar=c(0,4,1,1))
barplot(histx$counts, axes=FALSE, ylim=c(0, maxcounts), space=0)
par(mar=c(4,0,1,1))
barplot(histy$counts, axes=FALSE, xlim=c(0, maxcounts), space=0, horiz=TRUE)
dev.off()
lx = length(x)
makebiased = (lx-1)/lx
varx = var(x)*makebiased
vary = var(y)*makebiased
corxy <- cor.test(x,y,method='pearson')
cxy <- as.matrix(corxy$estimate)[1,1]
load(file='createtable')
a<-table.start()
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Pearson Product Moment Correlation - Ungrouped Data',3,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Statistic',1,TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,'Variable X',1,TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,'Variable Y',1,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,hyperlink('arithmetic_mean.htm','Mean',''),header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,mean(x))
a<-table.element(a,mean(y))
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,hyperlink('biased.htm','Biased Variance',''),header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,varx)
a<-table.element(a,vary)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,hyperlink('biased1.htm','Biased Standard Deviation',''),header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,sqrt(varx))
a<-table.element(a,sqrt(vary))
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,hyperlink('covariance.htm','Covariance',''),header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,cov(x,y),2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,hyperlink('pearson_correlation.htm','Correlation',''),header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,cxy,2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,hyperlink('coeff_of_determination.htm','Determination',''),header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,cxy*cxy,2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,hyperlink('ttest_statistic.htm','T-Test',''),header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,as.matrix(corxy$statistic)[1,1],2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'p-value (2 sided)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,(p2 <- as.matrix(corxy$p.value)[1,1]),2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'p-value (1 sided)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,p2/2,2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Degrees of Freedom',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,lx-2,2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Number of Observations',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,lx,2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.end(a)
table.save(a,file='mytable.tab')
|