gp <- function(lambda, p)
{
(p^lambda-(1-p)^lambda)/lambda
}
sortx <- sort(x)
c <- array(NA,dim=c(201))
for (i in 1:201)
{
if (i != 101) c[i] <- cor(gp(ppoints(x), lambda=(i-101)/100),sortx)
}
bitmap(file='test1.png')
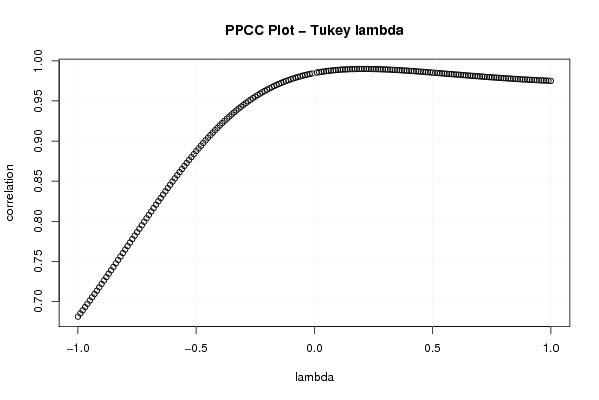
plot((-100:100)/100,c[1:201],xlab='lambda',ylab='correlation',main='PPCC Plot - Tukey lambda')
grid()
dev.off()
load(file='createtable')
a<-table.start()
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Tukey Lambda - Key Values',2,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Distribution (lambda)',1,TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,'Correlation',1,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Approx. Cauchy (lambda=-1)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,c[1])
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Exact Logistic (lambda=0)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,(c[100]+c[102])/2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Approx. Normal (lambda=0.14)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,c[115])
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'U-shaped (lambda=0.5)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,c[151])
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Exactly Uniform (lambda=1)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,c[201])
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.end(a)
table.save(a,file='mytable.tab')
|