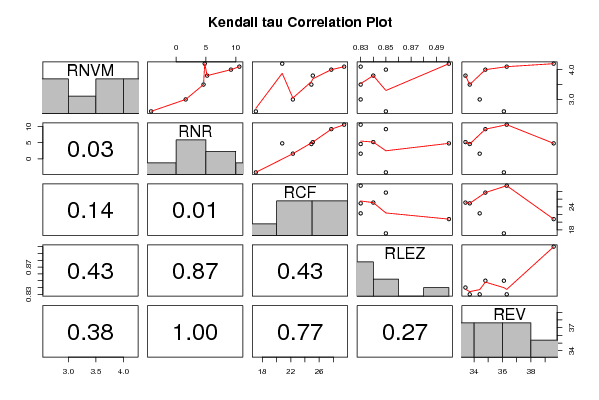
panel.tau <- function(x, y, digits=2, prefix='', cex.cor)
{
usr <- par('usr'); on.exit(par(usr))
par(usr = c(0, 1, 0, 1))
rr <- cor.test(x, y, method='kendall')
r <- round(rr$p.value,2)
txt <- format(c(r, 0.123456789), digits=digits)[1]
txt <- paste(prefix, txt, sep='')
if(missing(cex.cor)) cex <- 0.5/strwidth(txt)
text(0.5, 0.5, txt, cex = cex)
}
panel.hist <- function(x, ...)
{
usr <- par('usr'); on.exit(par(usr))
par(usr = c(usr[1:2], 0, 1.5) )
h <- hist(x, plot = FALSE)
breaks <- h$breaks; nB <- length(breaks)
y <- h$counts; y <- y/max(y)
rect(breaks[-nB], 0, breaks[-1], y, col='grey', ...)
}
bitmap(file='test1.png')
pairs(t(y),diag.panel=panel.hist, upper.panel=panel.smooth, lower.panel=panel.tau, main=main)
dev.off()
load(file='createtable')
a<-table.start()
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Kendall tau rank correlations for all pairs of data series',3,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'pair',1,TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,'tau',1,TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,'p-value',1,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
n <- length(y[,1])
n
cor.test(y[1,],y[2,],method='kendall')
for (i in 1:(n-1))
{
for (j in (i+1):n)
{
a<-table.row.start(a)
dum <- paste('tau(',dimnames(t(x))[[2]][i])
dum <- paste(dum,',')
dum <- paste(dum,dimnames(t(x))[[2]][j])
dum <- paste(dum,')')
a<-table.element(a,dum,header=TRUE)
r <- cor.test(y[i,],y[j,],method='kendall')
a<-table.element(a,r$estimate)
a<-table.element(a,r$p.value)
a<-table.row.end(a)
}
}
a<-table.end(a)
table.save(a,file='mytable.tab')
|