Free Statistics
of Irreproducible Research!
Description of Statistical Computation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author's title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author | *The author of this computation has been verified* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R Software Module | rwasp_notchedbox1.wasp | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
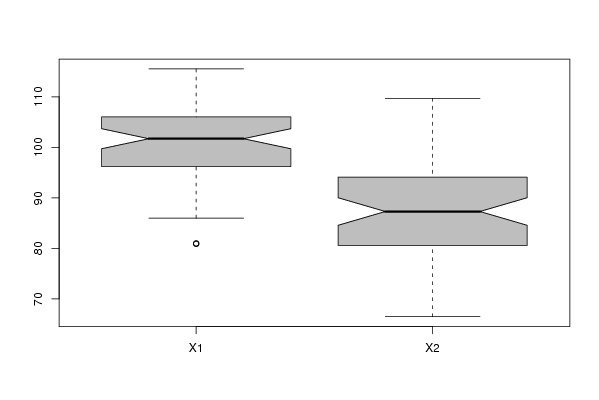
| Title produced by software | Notched Boxplots | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date of computation | Mon, 03 Nov 2008 04:08:49 -0700 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cite this page as follows | Statistical Computations at FreeStatistics.org, Office for Research Development and Education, URL https://freestatistics.org/blog/index.php?v=date/2008/Nov/03/t1225710586pj92wfvpyzmucaw.htm/, Retrieved Sun, 19 May 2024 10:42:28 +0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistical Computations at FreeStatistics.org, Office for Research Development and Education, URL https://freestatistics.org/blog/index.php?pk=20822, Retrieved Sun, 19 May 2024 10:42:28 +0000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QR Codes: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Original text written by user: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IsPrivate? | No (this computation is public) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| User-defined keywords | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Estimated Impact | 168 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tree of Dependent Computations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Family? (F = Feedback message, R = changed R code, M = changed R Module, P = changed Parameters, D = changed Data) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| F [Notched Boxplots] [workshop 3] [2007-10-26 13:31:48] [e9ffc5de6f8a7be62f22b142b5b6b1a8] F D [Notched Boxplots] [Workshop 4 Q1] [2008-11-03 11:08:49] [60d772482829eb846b04c71947363055] [Current] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Feedback Forum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Post a new message | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dataset | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dataseries X: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
110,40 109,20 96,40 88,60 101,90 94,30 106,20 98,30 81,00 86,40 94,70 80,60 101,00 104,10 109,40 108,20 102,30 93,40 90,70 71,90 96,20 94,10 96,10 94,90 106,00 96,40 103,10 91,10 102,00 84,40 104,70 86,40 86,00 88,00 92,10 75,10 106,90 109,70 112,60 103,00 101,70 82,10 92,00 68,00 97,40 96,40 97,00 94,30 105,40 90,00 102,70 88,00 98,10 76,10 104,50 82,50 87,40 81,40 89,90 66,50 109,80 97,20 111,70 94,10 98,60 80,70 96,90 70,50 95,10 87,80 97,00 89,50 112,70 99,60 102,90 84,20 97,40 75,10 111,40 92,00 87,40 80,80 96,80 73,10 114,10 99,80 110,30 90,00 103,90 83,10 101,60 72,40 94,60 78,80 95,90 87,30 104,70 91,00 102,80 80,10 98,10 73,60 113,90 86,40 80,90 74,50 95,70 71,20 113,20 92,40 105,90 81,50 108,80 85,30 102,30 69,90 99,00 84,20 100,70 90,70 115,50 100,30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tables (Output of Computation) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures (Output of Computation) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Input Parameters & R Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameters (Session): | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| par1 = grey ; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameters (R input): | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| par1 = grey ; par2 = ; par3 = ; par4 = ; par5 = ; par6 = ; par7 = ; par8 = ; par9 = ; par10 = ; par11 = ; par12 = ; par13 = ; par14 = ; par15 = ; par16 = ; par17 = ; par18 = ; par19 = ; par20 = ; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R code (references can be found in the software module): | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
z <- as.data.frame(t(y)) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||